By submitting your email you agree to receive information about relevant products and services. You may unsubscribe at any time. Read our Privacy Policy here.
The Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) is a framework of requirements used in the automotive supply chain to establish confidence in suppliers and their manufacturing processes.
The purpose of the PPAP is to ensure that the customer's design has been understood by the supplier and to prove that the supplier is capable of producing parts that meet all the requirements consistently.
A part drawing that is usually provided by the customer. Every feature on the part drawing must be ballooned (or bubbled) to correspond with the inspection results. This includes print notes, standard tolerance notes and specifications, and anything else that is relevant to the design of the part.
Learn more about how to create a ballooned part drawing for PPAP.
Why include a copy of the part drawing in your PPAP? It shows your customer you have a copy of the part drawing and ensures you are both discussing the same part.
A document that shows the detailed description of the change, usually called an "Engineering Change Notice". This document is only required if there is a change.
This approval is usually the engineering trial with sample production parts performed by the customer. A "temporary deviation" is often required to send parts to the customer before the PPAP is complete. Your customer may require other additional engineering approvals.
Design Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (DFMEA) is an application of the Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) that is specific to the design stage. The DFMEA allows the design team to document what they predict about a product's potential failures before completing a design and use this information to mitigate the causes of failure.
The Process Flow Diagram shows all the steps required in the manufacturing of the part. It should include all of the main steps in the processing of the part including incoming components, measuring, and inspection. The Process Flow Diagram should match the control plan and the Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA) and also includes the flow of non-conforming materials and parts.
Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA) evaluates each step in the production process to indicate what could go wrong during the fabrication and assembly of each part.
The Control Plan mirrors the PFMEA (Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) and provides more details on how potential issues are checked in the incoming inspection, assembly process, or during the inspection of the finished part. Learn more about control plan requirements and download a free template.
The Measurement Systems Analysis is a study itself and will conform to the customer's relevant ISO or TS standard. Typically it includes the Gauge R&R (Gauge Repeatability and Reproducibility) for the critical characteristics and a confirmation that gauges used to measure these characteristics are calibrated.
A list of every dimension on the ballooned part drawing and measurement results. This list includes the product characteristic, specification, measurement results, and assessment showing if the dimension "passed" or "failed". Typically a minimum of 6 pieces are reported per product. Learn more about how to create a PPAP Dimensional Results Report.
A summary of all tests that have been performed on the part. The summary should document any pass or fail inspection results. It should be signed off by the customer and the supplier to show that all required tests have been done and any additional data for tests have been submitted.
Generally, this includes SPC (Statistical Process Control) charts for critical characteristics. These studies demonstrate that the critical processes are stable and are ready to begin the process validation builds.
Includes all of the industry certifications for any lab that was involved in completing validation testing.
The Appearance Approval Report verifies that the customer has inspected the final product and it meets all the required appearance specifications for the design. The report includes color, textures, fit (gaps between parts), etc.
A picture of the production parts is included in the PPAP documentation along with the location where the parts are stored.
A sample part that is signed off by the customer and supplier. The master part is normally used to train operators on subjective inspections such as visual or for noise.
Checking aids are used by production and are a detailed list of all the tools used to inspect test or measure parts during the assembly process. This aid will list the part, describe the tool, and have the calibration schedule for the tool.
This section of the PPAP requirements is where each customer lists their own specific requirements for the PPAP process.
The Part Submission Warrant is a summary of the entire PPAP submission and specifies:
Learn more about the Part Submission Warrant and download free PSW templates as Excel and PDF files.
PPAP (Production Part Approval Process) is one component of APQP (Advanced Product Quality Planning).
Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) is a defined process used for introducing a new product in the market or incorporating changes in the product after its release. A Cross-Functional Team (CFT) composed of engineering, manufacturing, quality, procurement, and distribution professionals performs an APQP to ensure that products meet customer requirements.
If the PPAP results don't meet customer expectations, that usually means the APQP process isn't working properly. The test for both APQP and PPAP is a production trial run. If the finished trial product includes defective parts, the manufacturer has to go over the supply chain and find out where PPAP or APQP went wrong.
What’s Included:
PPAP Excel Template with worksheets for the following elements:
What’s Included:
PPAP Excel Template with worksheets for the following elements:
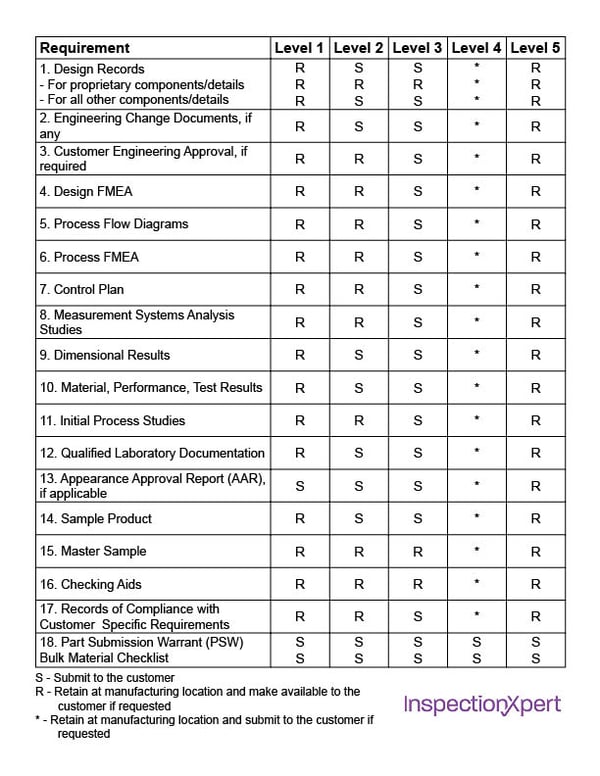
The PPAP Submission Levels indicate which documents need to be submitted to the customer, and which can simply be retained by the manufacturer. According to the AIAG PPAP manual, all elements should be completed.
Level 1 - Part Submission Warrant (PSW) only
Level 2 - PSW with product samples and limited supporting data
Level 3 - PSW with product samples and complete supporting data
Level 4 - PSW and other requirements as defined by the customer
Level 5 - PSW with product samples and complete supporting data available for review at the supplier's manufacturing location
Balloon your part drawing, capture feature data, and instantly publish to your Excel report.
Copyright 2026 Ideagen, All Rights Reserved